

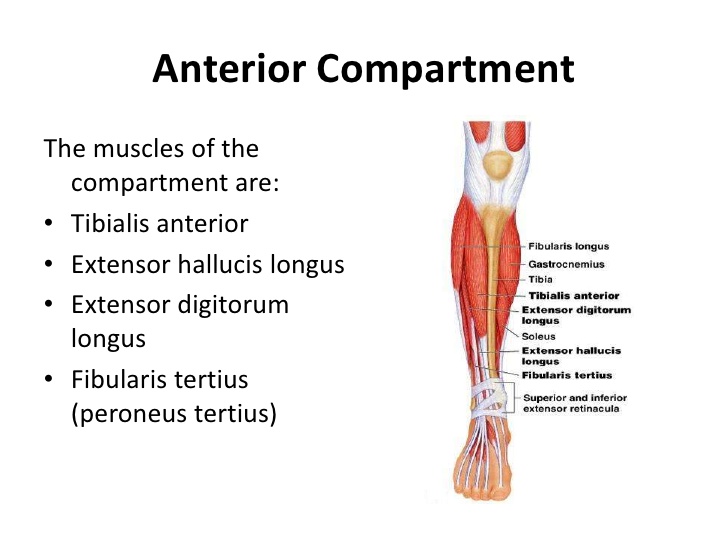
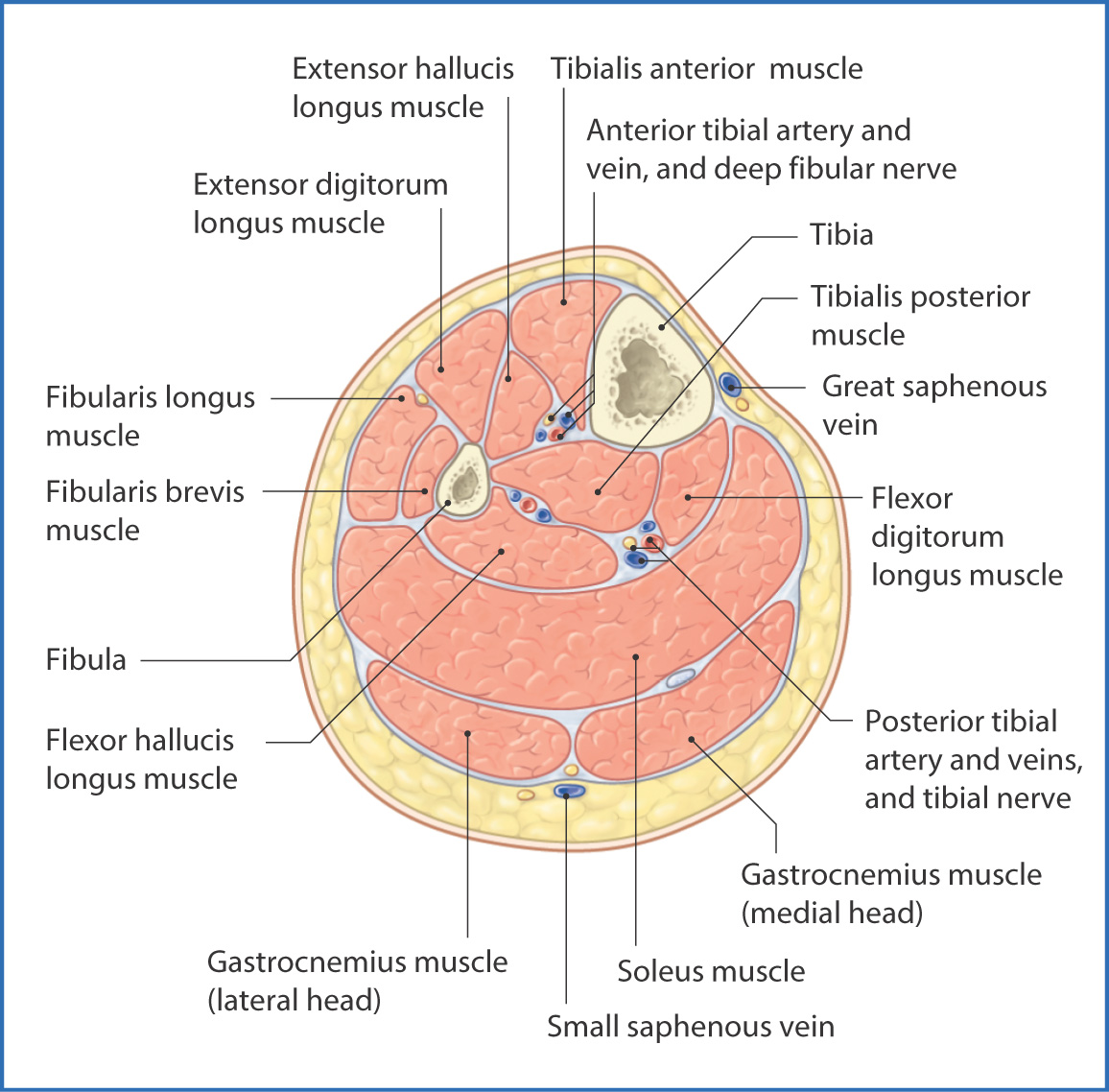
Skin of the plantar surface of the toes and dorsal surface of the distal interphalangeal segment (to the lateral side of the 5th toe)įlexor hallucis brevis m. (to the medial side of the great toe) superficial br. "peroneal" is old terminology which has been replaced by "fibular" anterior compartment syndrome - trauma to the anterior side of the leg can result in pressure buildup in the anterior compartment (from swelling or bleeding) that can damage the deep fibular n., resulting in "foot drop"Ĭommon plantar digital medial plantar n. Skin of the web between the great toe and the 2nd toe Muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg (tibialis anterior m., extensor hallucis longus m., extensor digitorum longus m., fibularis tertius m.) and muscles of the dorsum of the foot (extensor digitorum brevis m.and extensor hallucis brevis m.) The dorsal surfaces of the distal tips of the toes (nail bed regions) are supplied by the proper plantar digital brs. Skin of the plantar surface of the toes (except the medial side of the great toe and the lateral side of the 5th toe) "peroneal" is old terminology which has been replaced by "fibular" Superficial fibular n.: distal 1/3 of the anterior surface of the leg, dorsum of the foot excluding the web between the great toe and the 2nd toe and distal interphalangeal segments of all toes deep fibular n.: skin of the web between the great toe and the 2nd toe Superficial fibular n.: muscles of the lateral compartment of the leg (fibularis longus and brevis mm.) deep fibular n.: muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg (tibialis anterior m., extensor hallucis longus m., extensor digitorum longus m., fibularis tertius m.) and muscles of the dorsum of the foot (extensor digitorum brevis m.and extensor hallucis brevis m.) Lateral sural cutaneous n., superficial and deep fibular nn.
Only part of the S4 ventral primary ramus is contributed to the coccygeal plexus Ventral primary rami of spinal nerves S4, S5, C1
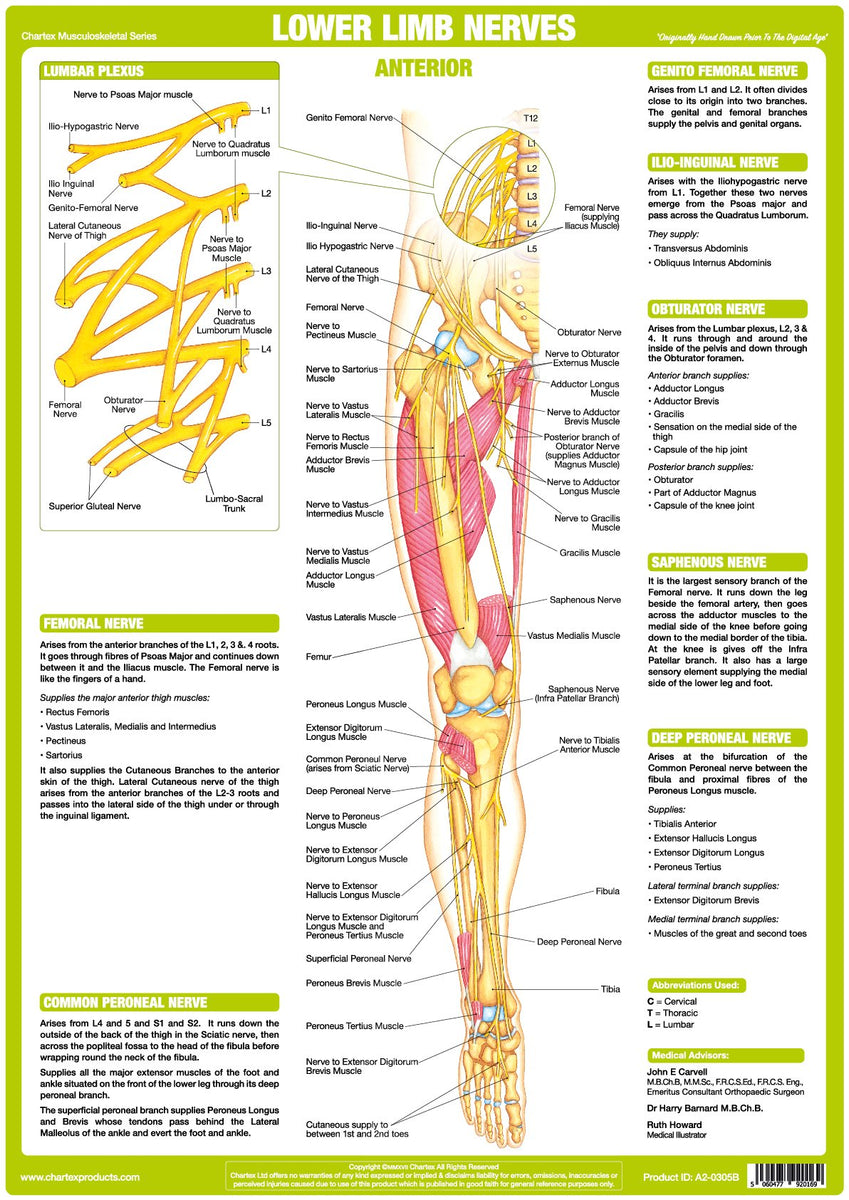
Skin of the superomedial portion of the buttock Skin of the intermediate medial portion of the buttock Lateral cutaneous branches of the dorsal primary rami of spinal nerves S1-3 carry postganglionic sympathetic axons to skin Innervation: Superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve.Cutaneous nn.Also supports the lateral and transverse arches of the foot. Actions: Eversion and plantarflexion of the foot.The tendon crosses under the foot, and attaches to the bones on the medial side, namely the medial cuneiform and base of metatarsal I.The fibres converge into a tendon, which descends into the foot, posterior to the lateral malleolus.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
